Fouling Factor in Heat Exchangers
2024-05-31 18:00:45

A detailed examination of fluid-induced fouling factors in heat exchangers. Fouling factor values for different fluids and their importance in heat exchanger design.
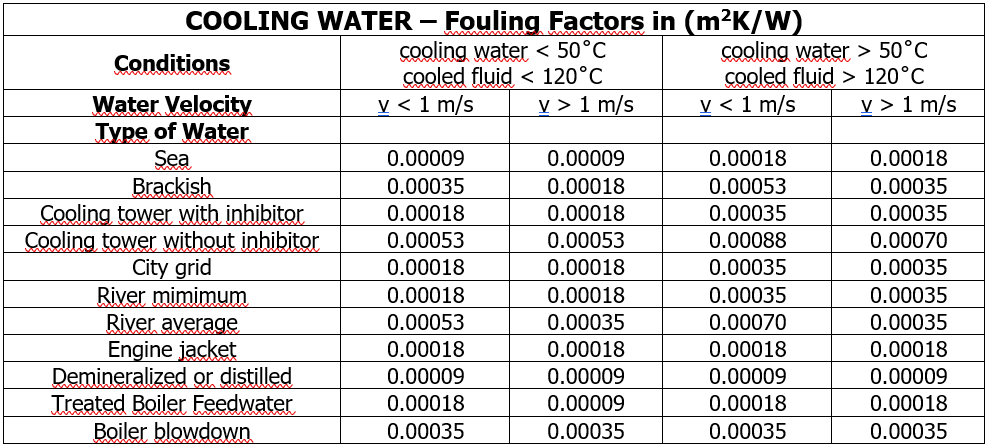
Factors and Importance of Fluid-Induced Fouling in Heat Exchangers
Heat exchangers are a general term for equipment that facilitates heat transfer. A range of factors can affect the efficiency and lifespan of these crucial systems. One such factor is fluid or process-induced fouling.
Fluid-induced fouling is a common issue in heat exchangers and can be caused by various factors. These include solid particles in the process fluids, sediment, corrosive products, and organic compounds. These fouling factors can adversely affect the performance of heat exchangers and potentially cause significant damage.
Fluid-induced fouling in heat exchangers can lead to several problems. Firstly, it can accumulate on heat exchanger surfaces, reducing heat transfer efficiency. This situation can result in energy loss and increased operating costs. Additionally, fouling can cause blockages within the heat exchangers or irregular fluid flow, leading to pressure loss in the system and even damage to the equipment.
The following list contains fouling factor values for heat exchanger design under different fluids, including more specific types. However, determining the most appropriate values for a specific application generally requires experience and careful analysis.
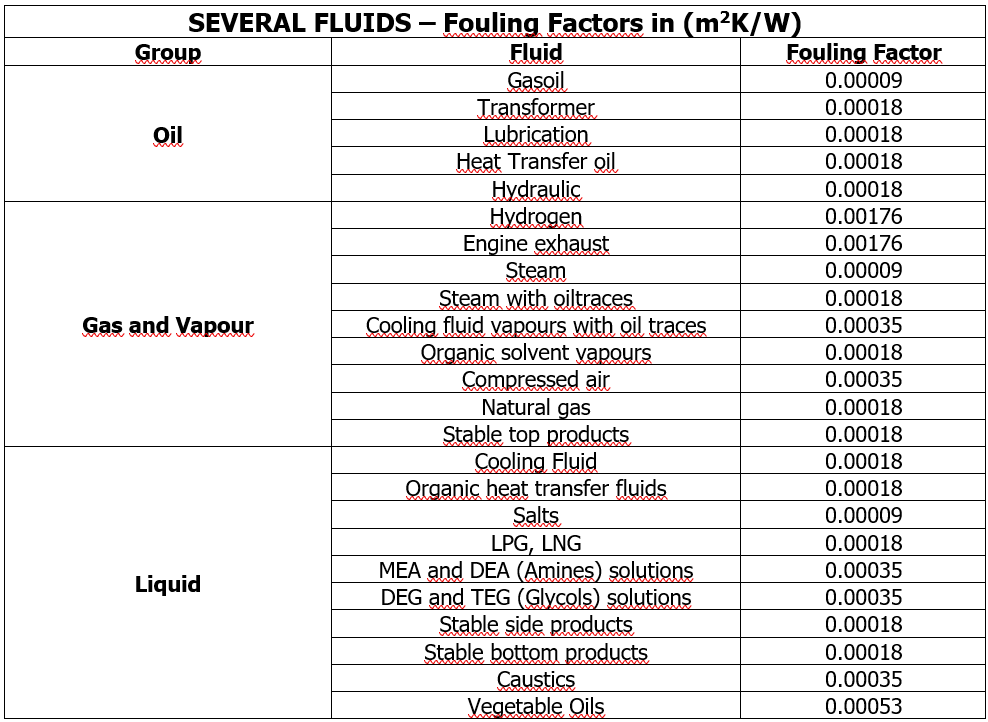
Managing fluid-induced fouling is vital for enhancing the performance of heat exchangers and reducing operating costs. Therefore, it is important to implement regular maintenance and cleaning routines along with appropriate filtration systems. Additionally, selecting suitable materials and using protective coatings can help mitigate the effects of fouling.
In conclusion, fluid-induced fouling factors in heat exchangers have a significant impact on the efficiency and reliability of energy systems. Therefore, businesses need to take these factors into account and implement appropriate measures and regular maintenance. Only in this way can heat exchangers be ensured to operate efficiently and have a long service life.