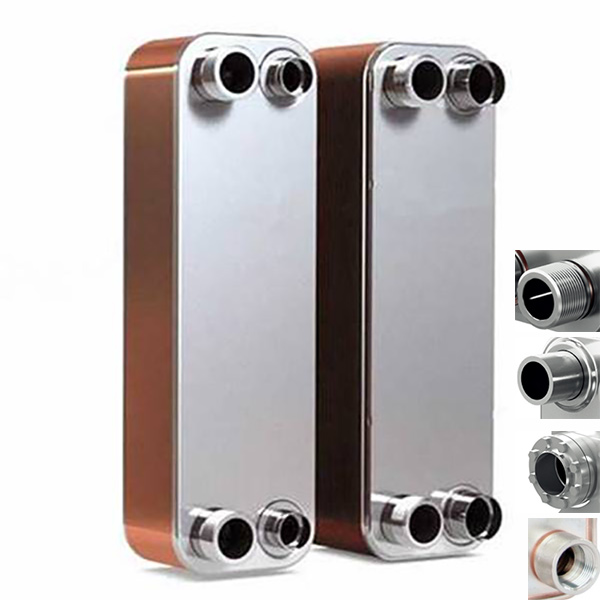
Brazed Heat Exchangers vs. Plate Heat Exchangers
2024-03-11 02:37:16

The differences between brazed heat exchangers and plate heat exchangers stand out with their reasons for preference and advantages.
Heat exchangers play a critical role in heat transfer and are vital equipment in various industrial applications. The differences between brazed heat exchangers and plate heat exchangers, along with the reasons and advantages of their preferences in different industrial applications, will be explained in a series of statements in this text.
Brazed Heat Exchangers and Plate Heat Exchangers Explained:
Brazed heat exchangers are equipment that facilitates heat transfer between two different fluids without mixing and ensures sealing using solder material between the plates. Due to their structure, they are more compact than plate heat exchangers regarding the tasks they perform. They are generally used for operating pressures up to 30 bars. Plate heat exchangers, on the other hand, allow heat transfer between two different fluids without mixing, and sealing is achieved using gaskets between the plates. Plate heat exchangers are produced according to pressure classes such as PN10, PN16, and PN25. Plate heat exchangers are more suitable for general installation requirements, and they are more advantageous in terms of maintenance due to their dismantling capability compared to brazed heat exchangers.
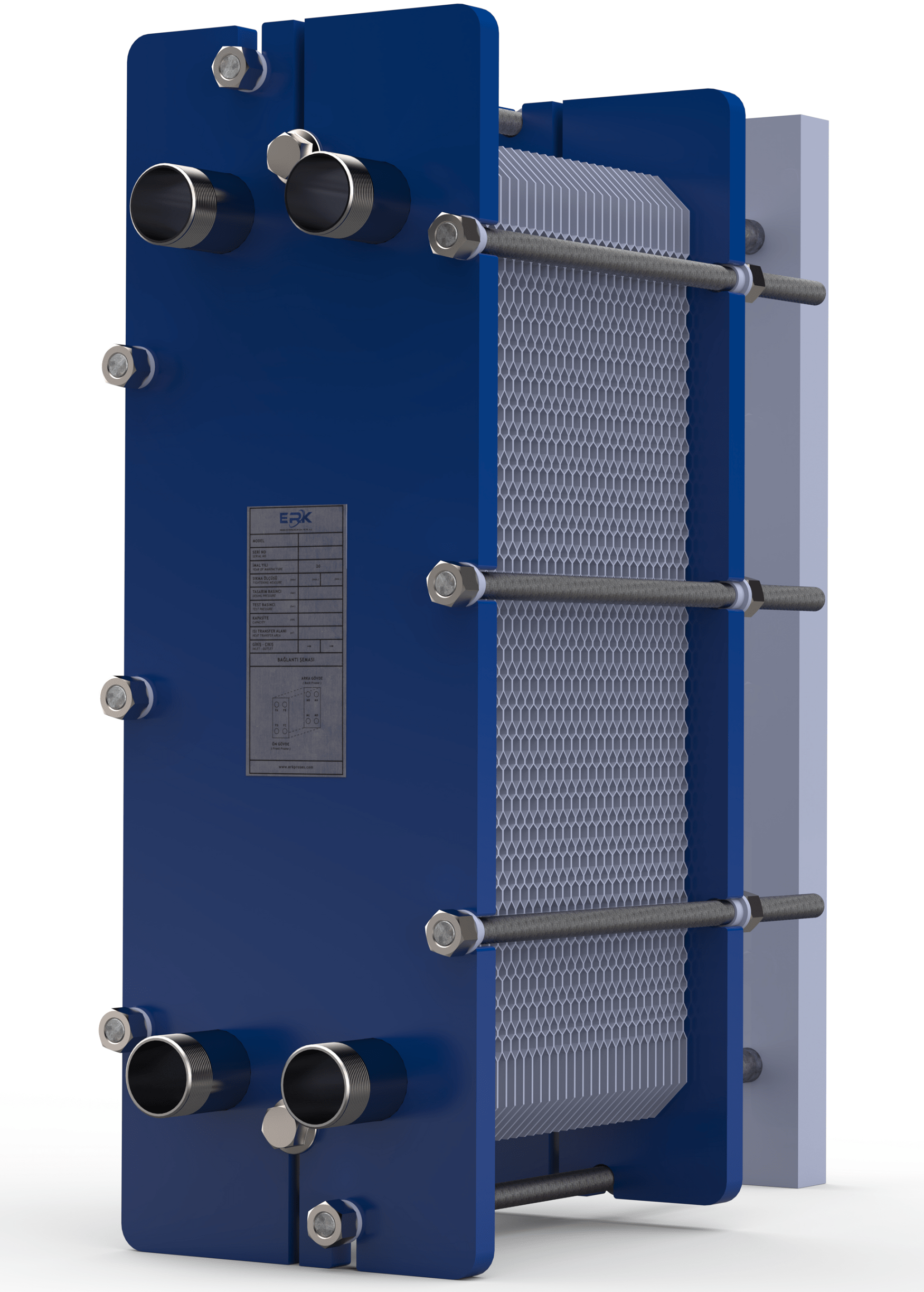
Structural Differences and Industrial Applications:
Although both heat exchanger groups have a similar structure, they have differences in their main assembly structures, used processes, and dimensions. The main feature that sets them apart is how the sealing is achieved. In brazed heat exchangers, the plates that provide heat transfer are connected to each other with copper or nickel solder material. Plate heat exchangers, on the other hand, create a structure by compressing gaskets between the front and back bodies. Due to their assembly structure, plate heat exchangers have a dismantling capability. However, the same ease of disassembly is not present in brazed heat exchangers.
Application Conditions and Usage in Industries:
The use of plate heat exchangers is more comprehensive compared to brazed heat exchangers. Plate heat exchangers can be used in various processes in sectors such as chemical, petrochemical, energy, HVAC, paper, pharmaceutical, iron-steel, food, dairy, beverage, automotive, maritime, mining, treatment, biogas, etc. Brazed heat exchangers, with their more compact structures, are used in certain tasks such as air conditioning sectors, floor heating or hot water production, where plate heat exchangers can perform some tasks but are structurally advantageous for certain applications that only brazed heat exchangers can provide.
Design and Manufacturing: Important Considerations
In the design of both heat exchangers, fluid characteristics, operating conditions, and durability should be prioritized. Material quality, assembly precision, and an effective design that provides long-lasting performance are important. These criteria should be considered, and the design process should be advanced by choosing between brazed or plate heat exchangers according to the requested specifications. In similar tasks where continuous maintenance is not required, and dirty fluids are not used in processes, brazed heat exchangers may be more cost-effective than plate heat exchangers. However, as mentioned at the beginning of the paragraph, considering the usage life criteria by evaluating process conditions, it is beneficial to make a choice.
Discover Excellence in Heat Transfer with ERK Process: Expertise, Reliability, and Innovation Together!
ERK Process has specialized in the design and manufacturing of brazed and plate heat exchangers, aiming to make a difference in the industry and considering providing benefits to its customers as a mission. With high-quality materials, excellent workmanship, and products that comply with industry standards, ERK Process offers reliable and efficient heat transfer solutions to its customers.
